What Is a Smart City? Definition and 6 Examples
Urbanization needs optimization. By 2050, 2 in 3 people across the world will live in cities, which will leave a strain on city resources. Although cities generate much of the world’s wealth, many cities aren’t prepared for their rapid growth. According to C40, 75% of all global energy consumption occurs in cities.
Smart cities could be the solution. A smart city model uses modern information and communication technology to improve its infrastructure, share information with the public and provide a better city living experience.
Smart City Technologies
Smart cities are implementing smart technologies in everything from street lamps and drones to robotics and building information modeling (BIM). And that’s just the beginning. The growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) is what makes smart cities just that — smart.
IoT describes the network of physical objects that use sensors, software, and other technologies to connect and exchange information with other systems by using the internet. Smart cities use such devices to collect and analyze data to improve infrastructure, public utilities, government-provided services, and the overall city life experience.
In fact, the value of IoT in smart cities is expected to reach $735 Billion by 2030, proving that cities are eager to embrace new tech that promotes sustainable growth.
Characteristics of Smart Cities
Collaborating with big-name developers like IBM, Microsoft, and Cisco and innovative startups, smart cities can track valuable data like weather, traffic, and resources. Then, they use it to optimize their energy use, utilities, safety, transportation, waste management, and public services. Let’s take a closer look at some of these smart city features.
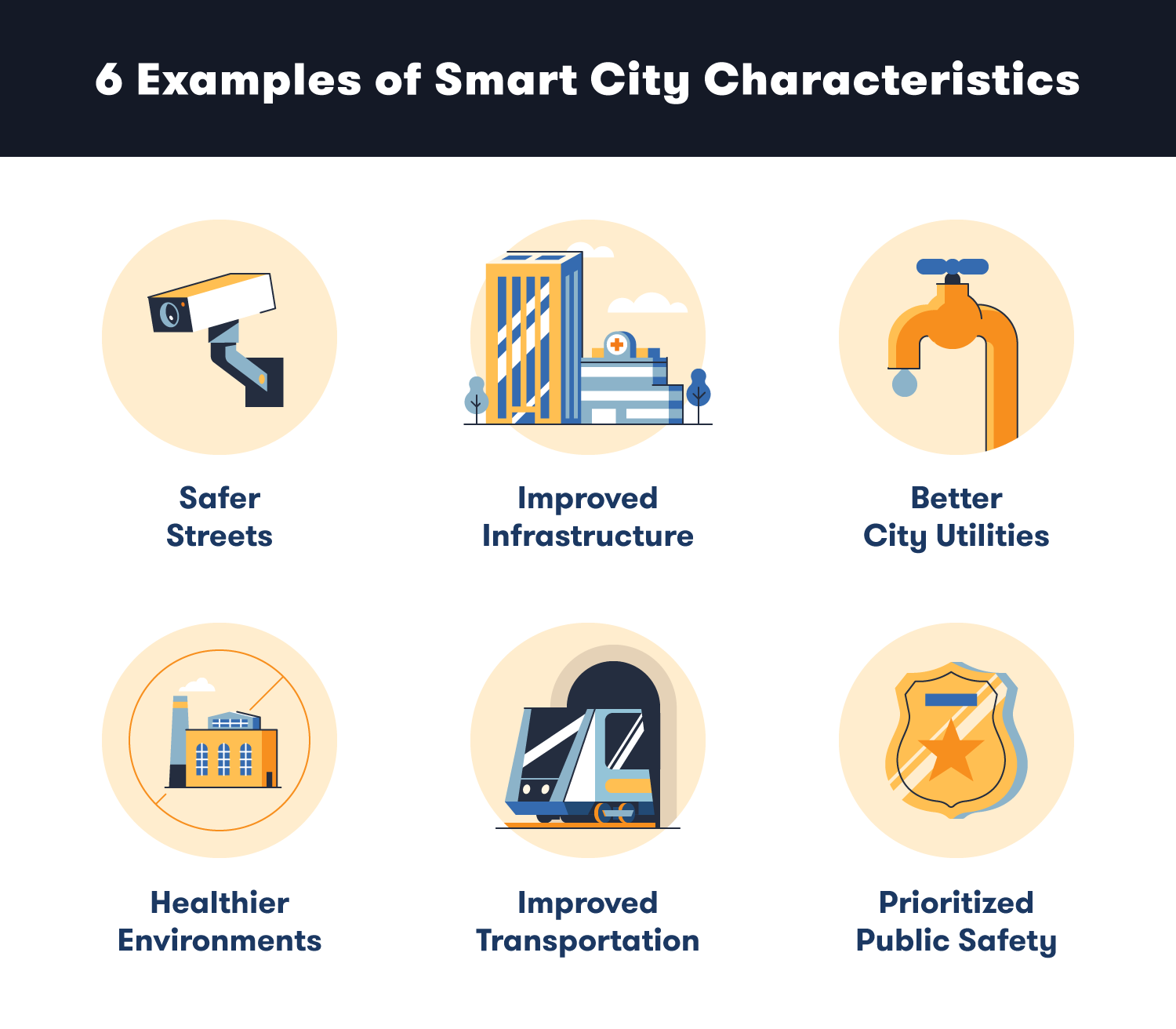
Safer Streets
Connected street cameras, body cameras, and commercial vehicles’ dashcams are all monitoring activity and sharing data in real-time. This data gives first responders and city officials the information they need to easily detect, respond to and prevent road accidents, violations, traffic jams, and even potholes.
Improved Infrastructure
In smart cities, an improved infrastructure allows resources to go further and allow for heightened safety preparedness. For example, resources like garbage collection can only be stretched so far in a typical city, making trash collection inaccessible for many. However, some smart cities are now using waste sensors to detect garbage levels and determine who needs garbage pick up and who doesn’t. Doing this allows garbage collectors to maximize their collection routes and serve more businesses and homes.
But improved infrastructure doesn’t stop with city services. It also allows for better city safety and structure, like structural sensors and smart earthquake detection to warn the public about incoming natural disasters well before they hit.
Better Utilities
Every home and business needs access to tap water, but what if your city went above and beyond to test and monitor it? Or what if the city monitored water levels, so city officials could become immediately aware of water leaks? This is a reality in some smart cities.
City lighting is also becoming increasingly smarter and more cost-effective, with LED lamp posts that adjust their brightness depending on the time of day and the weather conditions.
Smart cities are also adopting a “smart grid,” where energy consumption is analyzed to offer optimal electricity supplies at the right time to the right places.
Healthier Environment
Using air pollution sensors, smart cities can effectively monitor carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and car pollution. This monitoring allows city dwellers to redirect their traffic flow to avoid breathing in toxins, airborne illnesses, and other pollutants that can be detrimental to a person’s health.
Improved Transportation
Smart cities are all about efficiency. For many, transportation is a considerable efficiency waster. But with improved transportation methods like driverless cars, smart parking meters, and real-time traffic monitoring, people in some smart cities are getting time back in their day when they no longer have to waste time sitting in congested areas or looking for an open parking meter.
Prioritized Public Safety
If a city is striving to make itself more liveable, it has to guarantee better law enforcement and emergency response to increase public safety. Smart cities are using emergency cameras to give dispatchers and first responders optimal routes to scenes like car accidents, fires, natural disasters, crime scenes, and other emergencies. Smart city features are always evolving as cities adapt and adopt new technologies.
How Does a Smart City Work?
Smart cities use four key elements to become more livable as larger amounts of people continue to move to urban areas.
- Collection: Real-time data is collected by smart cameras and sensors.
- Analysis: Data is analyzed to understand and identify pain points and what can be improved.
- Communication: Once data is collected and analyzed, solutions are proposed to decision-makers and city officials.
- Action: Action plans are put in place to improve the quality of life for the city population.
These elements are the stepping stones to the innovations we see in smart cities today. As cities incorporate this methodology, city living across the world can become smarter, more sustainable and more efficient.
Smart City Examples
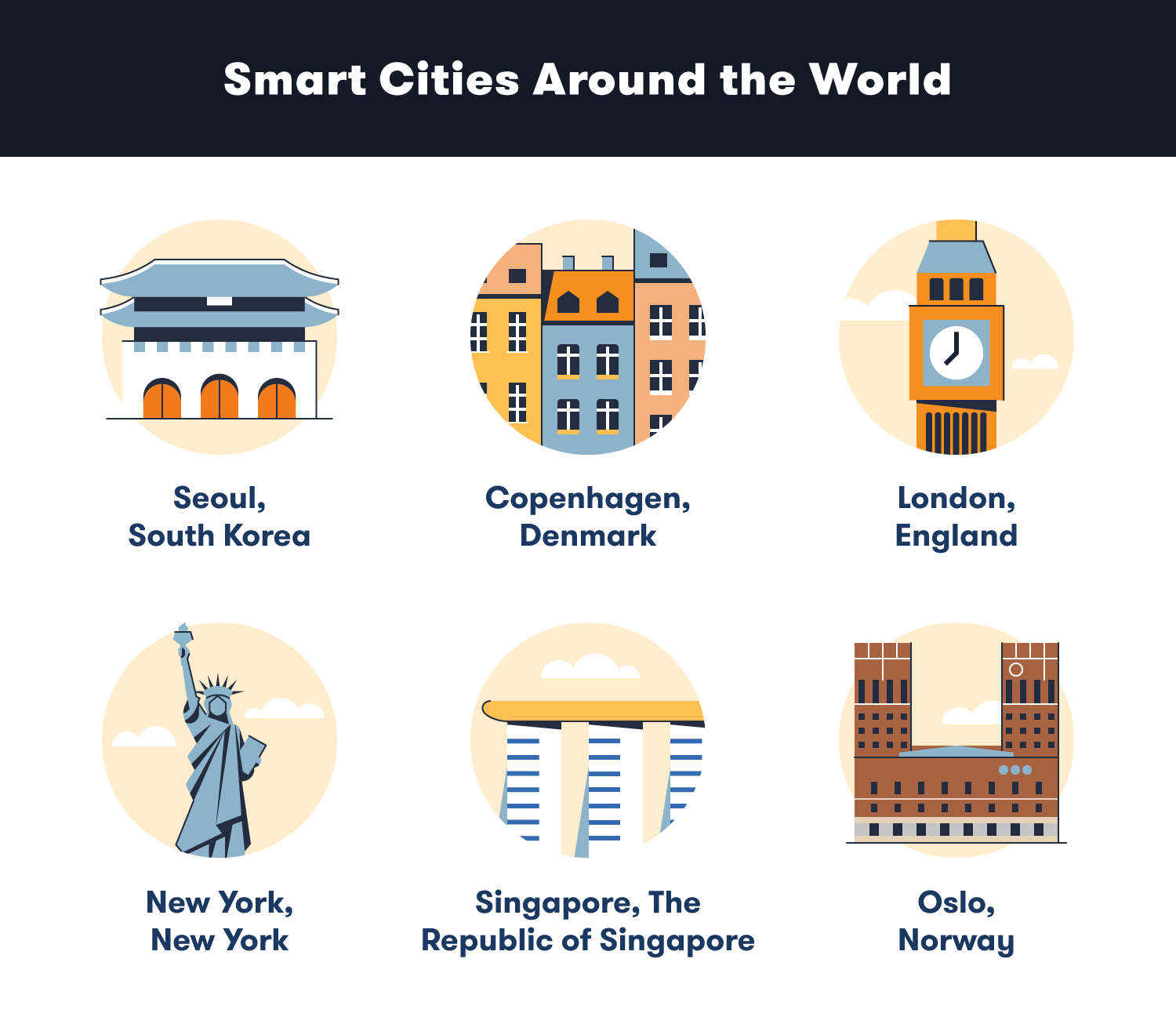
Seoul, South Korea
It shouldn’t be a surprise to see this city at the top of the list, as Seoul, South Korea was awarded Smart City of 2022 at Smart City Expo World Congress. Seoul is home to the highest broadband penetration rates and fastest internet speeds of all major cities across the globe. The city is highly admired for its advanced e-governance system that gives them access to an array of databases, government services, and online citizen engagement opportunities.
Seoul is also known for its highly advanced public transportation. Recent additions have included air quality filters, free phone changers, and enhanced wifi in passenger cars. To top it off, Seoul will soon be the first city to offer a car-hailing service with autonomous driving vehicles by partnering with Hyundai Motor Group.
What Makes It Smart: Seoul, South Korea, prioritizes the health and well-being of its citizens, and they seek ways to make living and publicly commuting in the city a more efficient and pleasant experience.
Copenhagen, Denmark
Copenhagen’s journey to becoming a smart city is based largely on becoming more green and eco-friendly. In fact, Copenhagen’s main target is to become a carbon-neutral city by 2025.
Copenhagen authorities collect data about citizens, businesses, and real estate trends and use this digitized information to offer free access to public data to drive innovation for smart solutions that would benefit the city and its citizens.
What Makes It Smart: Copenhagen, Denmark, is actively encouraging citizens to innovate and create smart solutions that offset the effect urbanization has on climate change.
London, England
London, England is home to several smart city initiatives. The Civic Innovation Challenge aims to encourage and support entrepreneurs and start-ups to develop smart solutions to the issue the city faces as a result of growing urbanization.
Another initiative is Connect London, which set a goal to provide 5G connectivity and modernize the city by fitting lamp posts with automated sensors and offering more electric vehicle charging stations.
The London Plan provides more details on how the city plans to innovate and adapt to an ever-growing population by improving healthcare, transportation and energy management.
What Makes It Smart: London is aware of its ever-growing population and is taking steps to implement already available technologies while supporting innovations that make city living more connected and convenient.
New York, New York, USA
New York City’s smart city project first took place in 2020, when hundreds of smart sensors were installed throughout the city. The goal of these sensors is to collect data and help manage city services like waste management and collection. The city is also taking steps to modernize outdated utilities, like replacing pay phone booths with wifi-enabled phone charging stations.
New York is also concerned about public safety and is testing software that uses historical data, terrain modeling and other collected data to predict and quickly respond to crime.
What Makes It Smart: While there is still room for improvement, New York is making great strides in strengthening its public resources like city-owned utilities and law enforcement.
Oslo, Norway
Oslo, like Copenhagen, has set its sights on becoming more sustainable and eco-friendly. One smart city improvement includes hundreds of thousands of LED lights that can intelligently adjust the amount of lighting based on current needs.
Oslo also plans to switch all vehicles in the city to electric-only by 2025. Considering the size and population of the city (about 1,086,000), this might seem like a lofty goal; however, their plan is well underway with data showing they are on track to reach this goal.
Not only are electric vehicles making a difference in Oslo’s transportation system, but the city also monitors cars to better understand traffic flow and find ways to reduce traffic congestion.
As Oslo grows, it embraces green building practices to allow for population growth without compromising its eco-friendly values.
What Makes It Smart: While sustainable cities and smart cities are not the same, Oslo is a great example of how smart city technologies can create a more sustainable living environment within a metropolitan area.
Singapore, The Republic of Singapore
Singapore is often considered the world’s smartest city. With its advanced economy, Singapore’s smart city initiatives seek to raise productivity. One example is their switch to a digital healthcare system that uses wearable devices and video consultations to care for patients remotely.
Singapore is also known for its plethora of sensors that can track information about the daily lives of citizens or track a certain area to know when it’s busiest. This data helps city officials understand the needs of their citizens solely based on their routines.
And lastly, Singapore is developing an eco-smart forest city that is vehicle-free and only walkable or cyclable. With over 42,000 homes planned, this no-vehicle zone is sure to draw some attention from eco-friendly city dwellers.
What Makes It Smart: Singapore is devoted to creating a technologically and environmentally friendly advanced city that, in a lot of ways, is far ahead of the curve. Singapore breeds new technologies and does not hesitate to put them to the test if they believe the tech will benefit its citizens.
Smart City Challenges
While the goal of a smart city is to make city living more accessible, making these large-scale updates and using tech that collects and shares large amounts of data can come with plenty of challenges along the way.
Here are five main challenges and concerns people have with smart city initiatives:
- Transparency: Collected and shared data must be accurate and shared in real time.
- Availability: Cities are responsible for installing sensors and smart cameras, but must also offer a reliable way for individuals and businesses to receive the data.
- Integrity: Data must not be manipulated by officials to paint the city in a more positive light.
- Confidentiality: Some collected data may not be intended for public consumption. Cities are responsible for keeping sensitive data private and secure from outside attacks.
- Accountability: Cities are responsible for who sees what data and how it’s used. Where there is highly-sensitive data, user logs should be enforced to ensure accountability for who accessed the data and how they plan to use it.
The Importance of Smart Cities
Big cities are becoming more aware of their growth. For example, London, England is projected to be home to 9.8 million people by 2043, an increase of 800 thousand people when compared with 2021. With that amount of growth, current cities do not have what it takes to make city living habitable.
Smart cities use intelligent technology, connected devices, and instantaneous data to solve real-world problems. From reducing energy use to alleviating traffic congestion, smart cities are positively changing the lives of urban residents worldwide.
Countries, towns, cities, and governments have realized the potential and impact of smart cities. Investment in smart cities is rapidly growing, as global spending on these revolutionary initiatives and digital technologies are expected to hit $2.6 trillion worldwide by 2026. Additionally, construction jobs in cities across the U.S. are booming to meet this demand.
With cost, sustainability, and efficiency benefits, smart city technologies are no longer part of the distant future. They are quickly becoming essential for cities to thrive and support a healthy, ever-growing population.
With the right technology and equipment, the construction industry is ready to take the next steps into the future as cities become smarter and more accessible for their citizens.